Sanctions Against Russia will Hurt European Economies: IMF

An economic slowdown in Russia due to the rising Western sanctions would affect Europe directly and indirectly, according to the International Monetary Fund.
The IMF said in a blog that the conflict in Ukraine and the related imposition of sanctions against Russia signal an escalation of geopolitical tensions that are already being felt in Russian financial markets.
"A deterioration in the conflict, with or even without a further escalation of sanctions and counter-sanctions, could have a substantial adverse impact on the Russian economy through direct and indirect (confidence) channels," the agency said in the blog.
The IMF noted that east European countries have the closest links with Russia and some of them could be seriously affected by a sharp slowdown in the Russian economy.
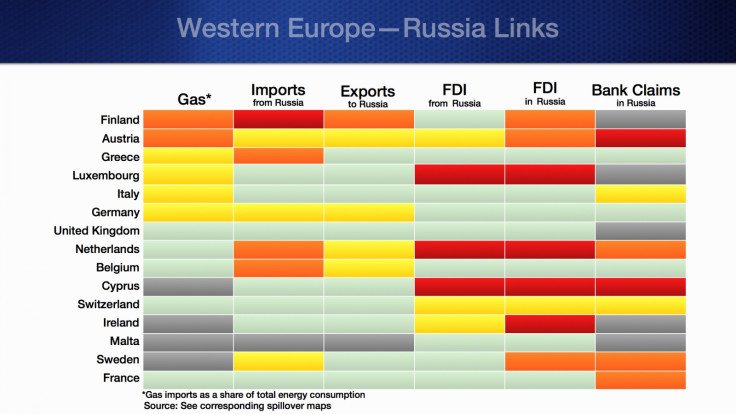
Western Europe is relatively less linked to Russia, but the countries in the region are still vulnerable.
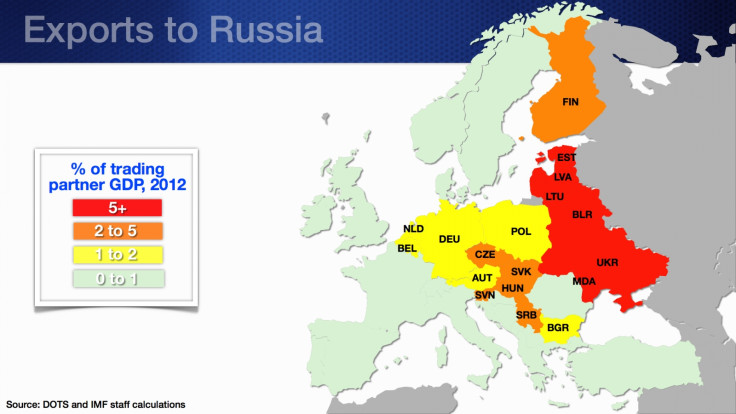
Exports of immediate neighbours such as Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova and the Baltics to Russia exceed 5% of their respective gross domestic product (GDP). Therefore, the impact on these countries could be substantial.
Energy Imports
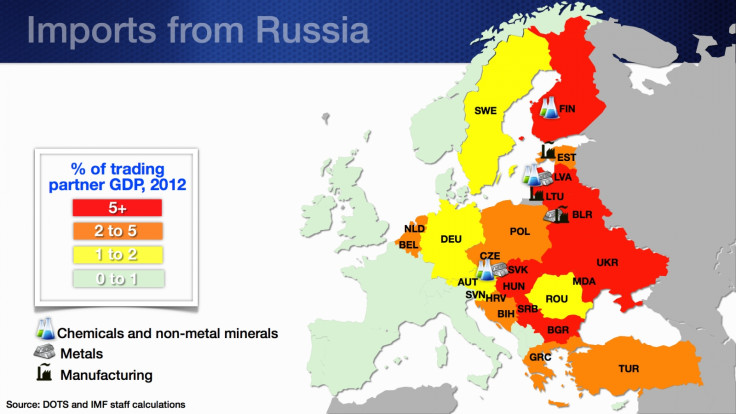
European countries depend more on Russia on the import side — particularly gas and oil. In addition, European companies dealing with chemicals, minerals, metals and manufacturing equipment rely heavily on inputs from Russia.
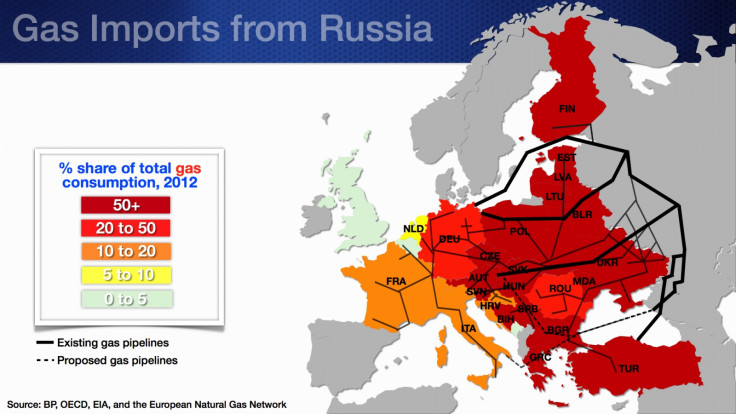
"Russian gas accounts for over 50% of total gas consumption in virtually all countries in Eastern Europe and several advanced economies in Europe as well," the IMF blog says.
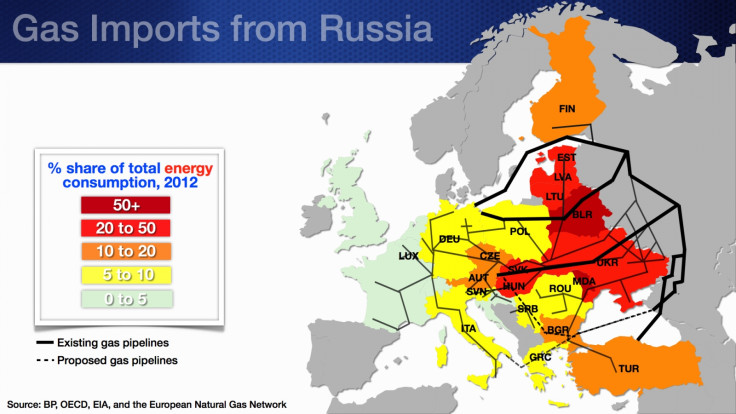
"However, as a share of total energy — rather than gas — consumption, Russian gas is somewhat less critical but still very important for several countries and especially so for Belarus and Moldova."
If Russia increases the price or cuts the supply of gas, European countries with less nimble energy infrastructure and relatively low gas inventories would suffer significantly, according to the IMF.
FDI to and from Russia
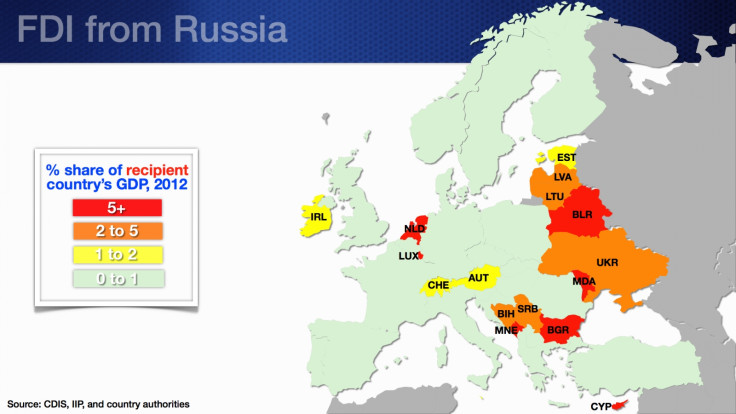
Foreign direct investment (FDI) from Russia, in industries such as banking, energy and metal and mining, exceeds 5% of the GDP for Belarus, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Montenegro.
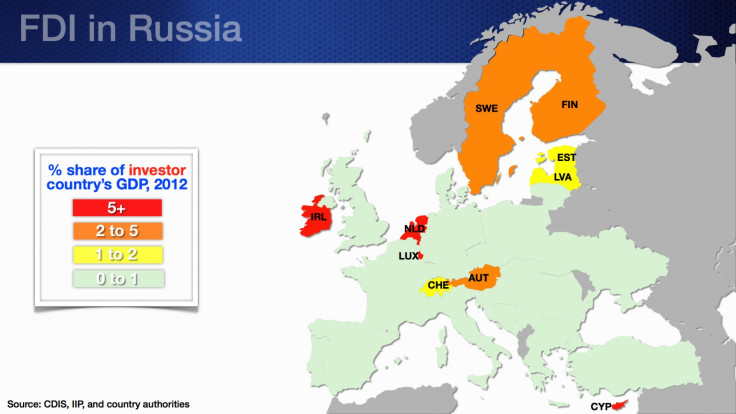
Advanced economies including the Netherlands and Ireland have significant FDI in Russia.
Banking Ties
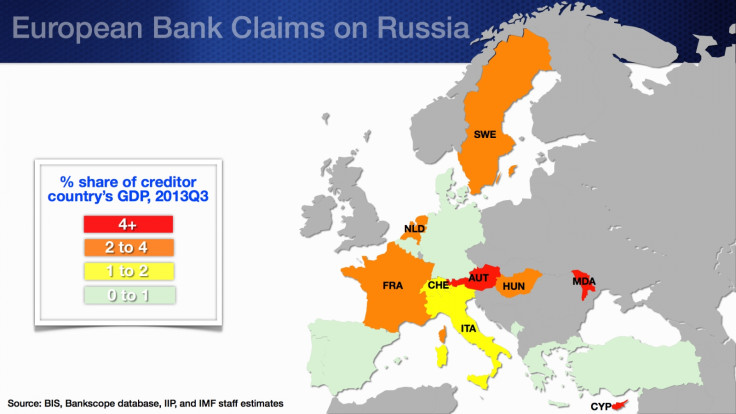
Many Western banks have sizable operations in Russia, accounting for more than a third of their yearly profits. Austrian, Hungarian, French and Italian banks have subsidiaries in Russia and also lend directly to customers in Russia from their branches outside Russia
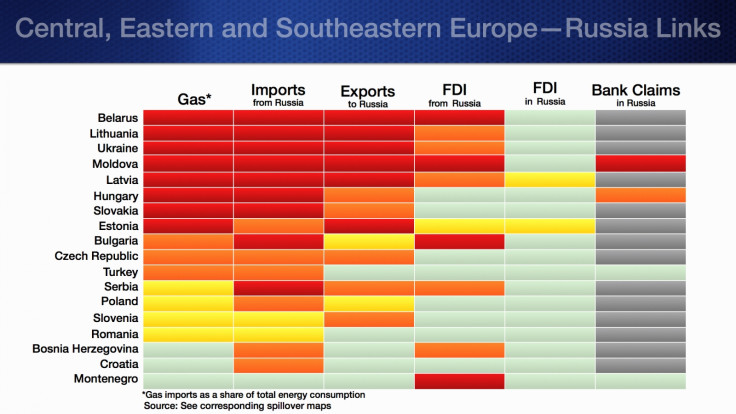
A summary of the Russia-Europe trade links is given below.
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.






















