Gliese 832 c: 'Best Habitable World Candidate' Discovered 16 Light Years Away
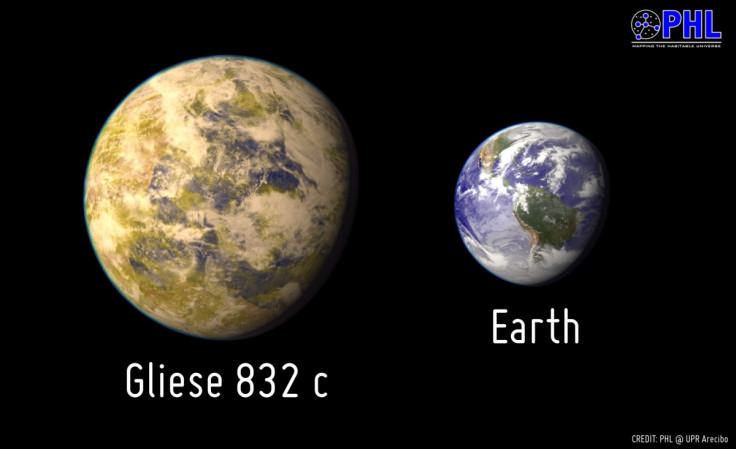

The "nearest best habitable world candidate" has been discovered by astronomers just 16 light years from Earth.
Gliese 832c was discovered by Robert A Wittenbyer from the University of New South Wales Australia, who found the planet has a mass of at least five times that of the Earth.
The planet orbits the red dwarf star Gliese 832 every 36 days and receives about the same amount of energy as the Earth does from the sun. "The planet might have Earth-like temperatures, albeit with large seasonal shifts, given a similar terrestrial atmosphere," the authors said.
"A denser atmosphere, something expected for Super-Earths, could easily make this planet too hot for life and a Super-Venus instead."
The planet is located near the inner edge of the habitable zone. The researchers said that while it could be habitable, it may also have a "massive atmosphere" that would render it inhospitable.
However, they added: "Gliese 832 c is the nearest best habitable world candidate so far."
The planet's Earth Similarity Index is similar to other planets, including Kepler-62e and Gliese 667 Cc: "This makes Gliese 832c one of the top three most Earth-like planets according to the ESI (i.e. with respect to Earth's stellar flux and mass) and the closest one to Earth of all three, a prime object for follow-up observations.
"However, other unknowns such as the bulk composition and atmosphere of the planet could make this world quite different to Earth and non-habitable."
The solar system of Gliese also has a cold Jupiter-like planet, meaning it is very similar to our solar system: "So far, the two planets of Gliese 832 are a scaled-down version of our own Solar System, with an inner potentially Earth-like planet and an outer Jupiter-like giant planet.
"The giant planet may well played a similar dynamical role in the Gliese 832 system to that played by Jupiter in our Solar System.
"It will be interesting to know if any additional objects in the Gliese 832 system follow this familiar Solar System configuration, but this architecture remains rare among the known exoplanet systems."
© Copyright IBTimes 2024. All rights reserved.






















