Chinese New Year 2015: Five ancient dinosaur discoveries in China during the year of the horse
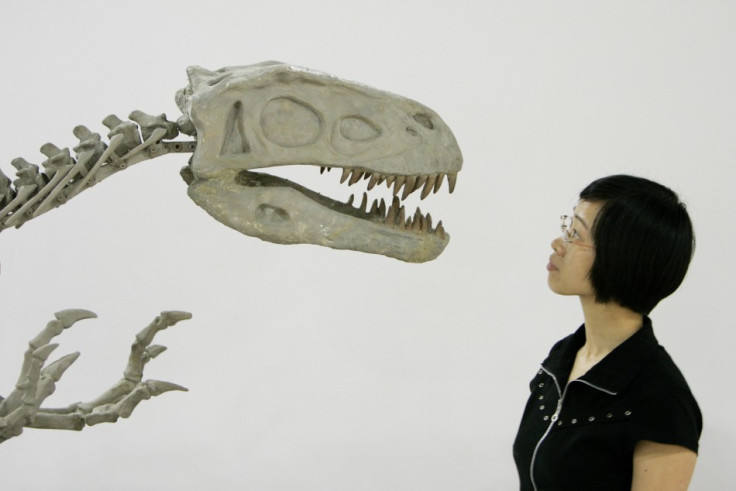

China is a nation exceptionally rich in dinosaur remains, with over 170 species excavated and named in the country over the past century. One of the best regions of the world to study the diverse group of creatures, dinosaur egg fossils in China account for one-third of the total found so far.
Dinosaurs first appeared during the Triassic period around 231.4 million years ago, and were the dominant vertebrates on earth for 135 million years – until the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event led to their extinction.
As we approach the Chinese New Year, we say goodbye to the year of the horse – a year which has seen the discovery and study of several incredible dinosaur species in China.
Qijianglong
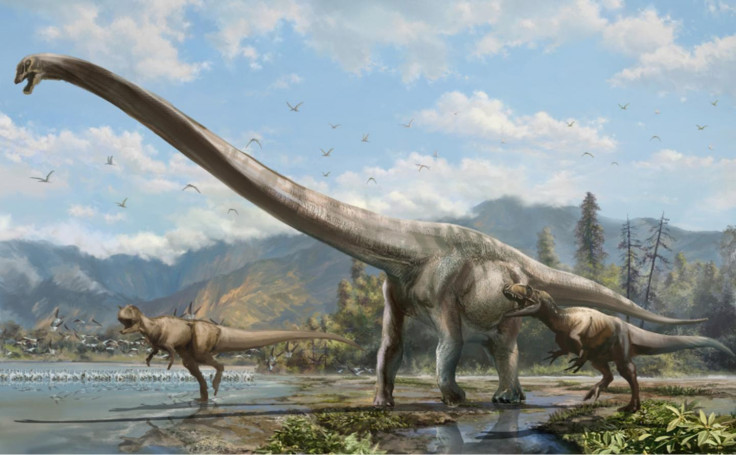

In January 2015, paleontologists found that a 50-foot "dragon" dinosaur species, discovered by farmers digging a fish pond in Qijiang city in the southwest Chongqing province, dated back to 160 million years ago.
Lida Xing, a member of the research team from the University of Alberta, told CNN it was named Qijianglong the "dragon of Qijiang", because the farmers believed the bones resembled the shape of Chinese mythical dragons. Researchers founds the new species belongs to a group of dinosaurs called mamenchisaurids, a family of sauropod dinosaurs with extremely long necks.
Pinocchio rex
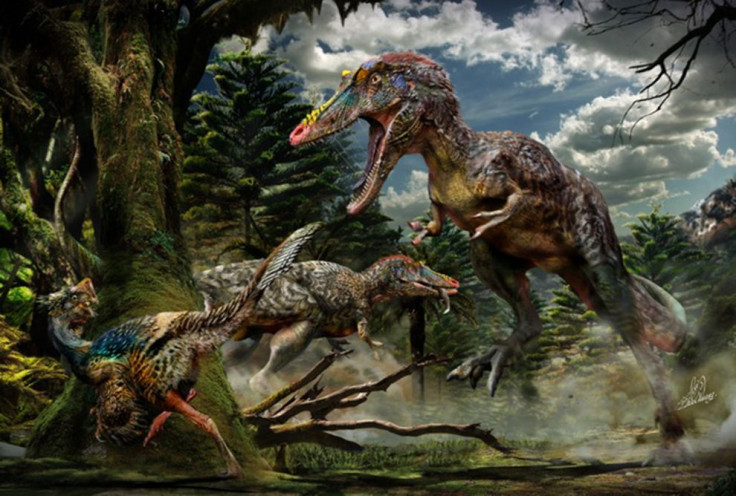

The remains of a long-nosed dinosaur, a cousin of the famous Tyrannosaurus rex, was discovered in southern China in May 2014. Nicknamed Pinocchio rex, Qianzhousaurus sinensis is believed to have roamed the earth during the late Cretaceous period around 66 million years ago.
With a long skull and narrow, sharp teeth, palaeontologists from the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences and the University of Edinburgh said the dinosaur is understood to have been a ferocious carnivore. Pinocchio rex was around ten feet shorter than its cousin, T-rex.
Chuanqilong chaoyangensis
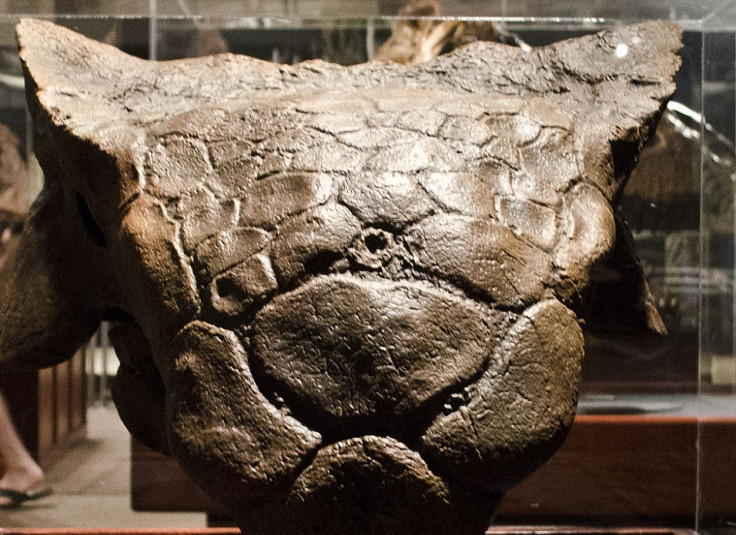

The skeleton of a 110-million-year-old ankylosaur was found in China last August, providing scientists with new information on the evolutionary history of the extinct creatures. Ankylosaurs were large, four-legged dinosaurs with an armoured shell, which existed from the early Jurassic period.
Some ankylosaurs have a large club at the end of their tail. As it was lacking in this specimen, named Chuanqilong chaoyangensis, it appears to be absent - an indication that this fossil is an early evolutionary example of the species. The fossil, found in a quarry by farmers in the Liaoning province, measures around 14.7 feet in length and is believed to be of a young dinosaur.
Yongjinglong datangi
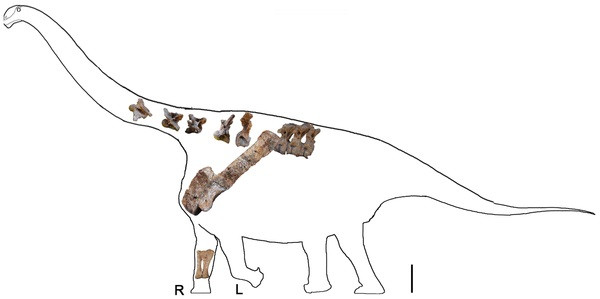
Chinese scientists in February 2014 identified the largest species of dinosaur that inhabited earth. The giant plant-eater, called Yongjinglong datangi, was around 60 feet in length and belonged to the family of a sauropod Titanosaurs. It was discovered in China's Gansu Province and believed to have lived around 100 million years ago.
The skeleton showed the dinosaur was a juvenile, suggesting the adult creatures were even larger. The research, led by a doctoral student, Liguo Li, and Dr Peter Dodson, who have affiliations with both the China University of Geosciences and the University of Pennsylvania, showed the shoulder blade of the animal was nearly two metres wide.
Changyuraptor yangi
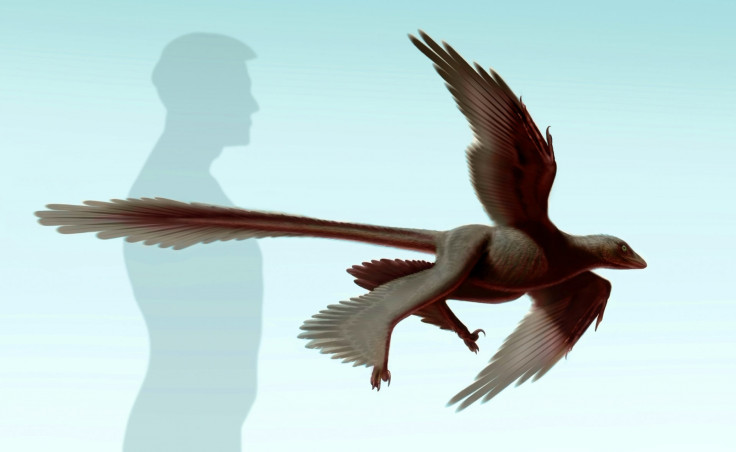

A four-winged flying dinosaur, the largest flying reptile of its kind, was discovered in July 2014 in the Liaoning Province in northeast China. Described by researchers as a "big turkey with a really long tail", Changyuraptor yangi was around 60% larger than the previous record holder Microraptor zhaoianus – of which many well-preserved remains have been found in China. It lived around 125 million years ago.
The fossil is understood to be an adult and is completely covered in feathers – including longer ones attached to its legs that give the appearance of a second set of "hind wings".
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.






















