Nexus 5 standby time improves with Android M

Google's new Android operating system brings improvement for the Nexus 5 in terms of battery, suggests test.
In an attempt to make the Android devices smarter about managing power, Google has introduced a new feature called Doze.
When an Android device is plugged and left stationary with the screen off for a while, it goes into Doze mode, which makes the system go into a sleep state. In this mode the device periodically resumes normal operations for brief periods of time so that app syncing can occur and the system can perform any pending operation. A few restrictions are applied to apps while the device is in Doze mode.
Another power saving feature is the App Standby wherein the system determines that apps are idle when they are not in active use. If a device is unplugged, apps deemed idle will have network access disabled and their syncs and jobs suspended. But when an Android device is plugged into a power source, these apps are allowed network access and can perform any job as well as syncs. If the device is idle for a long time, idle apps will get network access once a day.
To check how the Doze and App Standby help in battery life, German site Computerbase conducted tests for 48 hours on Nexus 5 running Android M preview against the same Nexus device on Android Lollipop version 5.1.1.
After eight hours the Nexus 5 powered with Android 5.1.1 consumed 4% battery, after 24 hours 12% and at the end of 48 hours the device had drained 24% power.
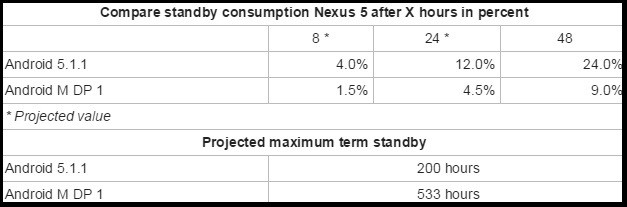
The Nexus 5 loaded with Android M developer preview drained just 1.5% in the first eight hours, 4.5% in 24 hours and a total of 9% when projected for 48 hours.
Furthermore, the Nexus 5 with Android 5.1.1 delivered 200 hours of standby against 533 hours of standby of the Android M drive handset. The Nexus 5 with new Android software provided 2.7% more standby time than on Android 5.1.1.
Hopefully, with the final release other Nexus devices like the Nexus 5 will bring optimum power management.
Source: Computerbase via PhoneArena
© Copyright IBTimes 2025. All rights reserved.





















