N.Ireland marks 25 years of peace, but police come under attack
Police vehicles were on Monday pelted with projectiles, including petrol bombs, during an illegal dissident republican march in Londonderry on the eve of Biden's visit.

Northern Ireland on Monday marked the 25th anniversary of its landmark 1998 peace accords, but the fragility of the province's truce was underlined as masked youths pelted police vehicles with petrol bombs during sectarian disorder.
No major public events are planned for the day itself, but British Prime Minister Rishi Sunak and US President Joe Biden will arrive Tuesday to launch several days of high-profile commemorations.
The territory has been reshaped since pro-UK unionist and pro-Irish nationalist leaders struck an unlikely peace deal on April 10, 1998 -- Easter Good Friday -- following marathon negotiations.
But the province has recently become mired in political dysfunction and security concerns that threaten to overshadow that milestone.
Underlining the threat, police vehicles were on Monday pelted with projectiles, including petrol bombs, during an illegal dissident republican march in Londonderry on the eve of Biden's visit.
"Our officers have come under attack...with petrol bombs and other objects thrown at their vehicle while in attendance at an un-notified Easter parade," said the Police Service of Northern Ireland (PSNI).
"No injuries have been reported at this time. We would appeal for calm," added police.
Officials last week warned of "strong" intelligence that dissidents were planning attacks against officers in the city on Monday.
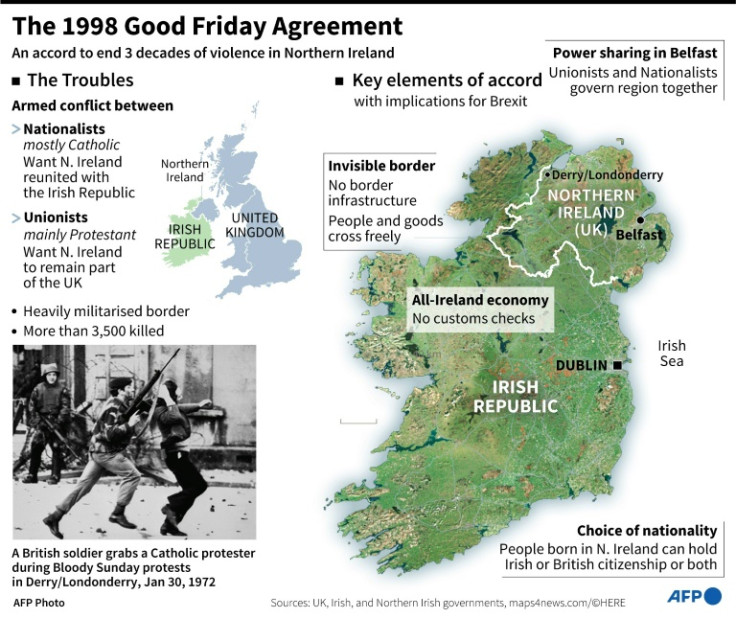
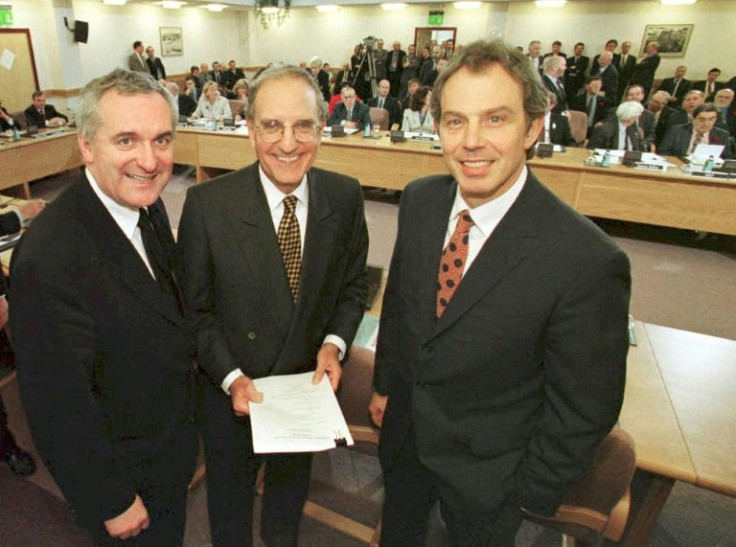
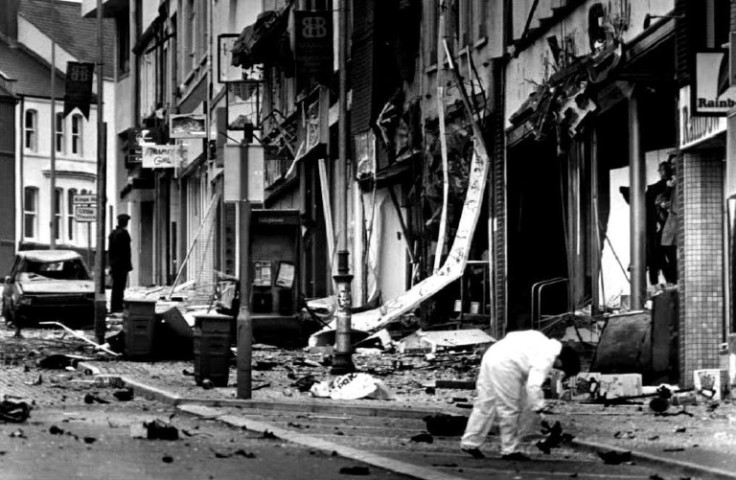
The Good Friday Agreement, brokered by Washington and ratified by governments in London and Dublin, largely ended three decades of devastating sectarian conflict in Northern Ireland and intermittent terrorist attacks on mainland Britain.

Known as "The Troubles", the conflict killed more than 3,500 people. It pitted the province's majority Protestant unionists, who support British rule, against Catholic republicans demanding equal rights and reunification with the Republic of Ireland.
A quarter-century on, Northern Ireland is struggling to consolidate the gains of its hard-earned peace. Post-Brexit trade arrangements have prompted political instability, and violence by dissident republicans is on the rise.
"While it is time to reflect on the solid progress we have made together, we must also recommit to redoubling our efforts on the promise made in 1998 and the agreements that followed," Sunak said in a statement marking Monday's anniversary.
"As we look forward, we will celebrate those who took difficult decisions, accepted compromise, and showed leadership."
Sunak will attend a commemorative conference at Queen's University in the capital, Belfast, and host a gala dinner to honour the anniversary, his Downing Street office has said.
Biden will "mark the tremendous progress since the signing of the Belfast/Good Friday Agreement," White House Press Secretary Karine Jean-Pierre told reporters ahead of his visit.
It will "underscore the readiness of the United States to support Northern Ireland's vast economic potential to the benefit of all communities", she added.
The Irish-American president will then travel south on Wednesday to Ireland, spending three days in his ancestral homeland.
While there he will "deliver an address to celebrate the deep, historic ties" the country shares with the US, said the White House.
Biden's visit will be closely scrutinised for any signs of pressure on Sunak to end the logjam in the North Ireland legislature caused by the Conservative Party's loyalist allies.
The following week, Northern Ireland will continue its peace accord commemorations with a three-day conference starting April 17 hosted by former US secretary of state Hillary Clinton.
Her husband, Bill Clinton, played a pivotal role in securing the 1998 deal as US president from 1993 to 2001.

The upcoming events will celebrate Northern Ireland's subsequent transformation, but focus will undoubtedly be drawn to its present woes.
In the years after 1998, Northern Irish paramilitaries were disarmed, its militarised border dismantled and British troops departed.
However, the peace process is perhaps more precarious now than it has been at any other point since then.
Power-sharing institutions created by the accords have been paralysed for more than a year over bitter disagreements on post-Brexit trade.
Despite Britain and the European Union agreeing in February to overhaul the arrangements, that new deal -- the Windsor Framework -- is yet to win the support of the pro-UK Democratic Unionist Party (DUP).
Irish Prime Minister Leo Varadkar said Sunday that Dublin, London and Belfast were "working towards having the institutions up and running in the next few months".
Meanwhile, the security situation has deteriorated, with Britain's security services last month raising the province's terror threat level to "severe".
© Copyright AFP 2025. All rights reserved.





















